Shimon Kolkowitz has already developed one of the most precise atomic clocks ever. Now, the UW–Madison physics professor has been awarded a Faculty Early Career Development (CAREER) award from the National Science Foundation (NSF) to …
Read the full article at: https://www.physics.wisc.edu/2021/12/15/shimon-kolkowitz-awarded-nsf-career-award/Year: 2021
An atomic clock measured how general relativity warps time across a millimeter
A record-breaking result reveals the precision achievable by atomic clocks, letting researchers detect slightly faster ticking over a tiny height change.
Read the full article at: https://www.sciencenews.org/article/atomic-clock-general-relativity-time-warp-millimeter-physicsA brand new flavor of optical lattice atomic clock: Xin and Jack’s paper posted to the arXiv!
Congratulations to Xin and Jack, as well as Kolkowitz group alums Brett, Haoran, and Varun, on the posting of their new paper “High precision differential clock comparisons with a multiplexed optical lattice clock” to the arXiv! You can find it here: http://arxiv.org/abs/2109.12237.
This paper describes the experimental realization of a new kind of optical atomic clock that consists of multiple clocks in one, and enables comparisons between these clocks at new levels of performance. For example, the paper includes a measurement of the fractional frequency difference between two clocks separated by ~6 mm at a precision below one part in 1019, or in other words at 20 digits of precision. This is a world record for the most precise frequency difference ever measured*, and represents a new regime of clock comparison stability and precision. To give a sense of scale, this corresponds to measuring a difference in the rate the two clocks are ticking at that would result in them disagreeing with each other by only 1 second after 300 billion years. This unprecedented metrological precision offers sensitivity to new and exotic physics. For example, this corresponds to the difference in the ticking rate between two otherwise identical clocks separated in height by only 1 millimeter due to general relativistic time dilation from Earth’s gravity field. The Kolkowitz group is currently hard at work measuring this effect!
You can read a lot more about these and other exciting results in the paper, but one thing you can’t do on the physics arXiv is watch cool movies! So here are some animated GIFs composed of actual camera images taken with our multiplexed optical lattice clock showing the procedure for preparing 2 clocks (left) and 6 clocks (right), which each clock (or ball) composed hundreds of strontium atoms trapped in an optical lattice at temperatures of just 1 millionth of a degree above absolute zero.
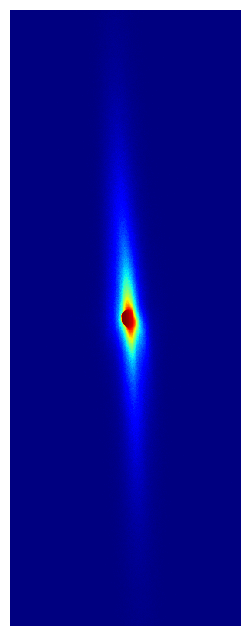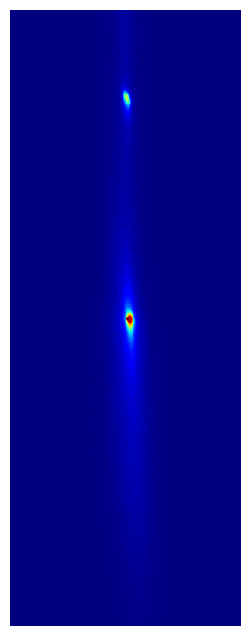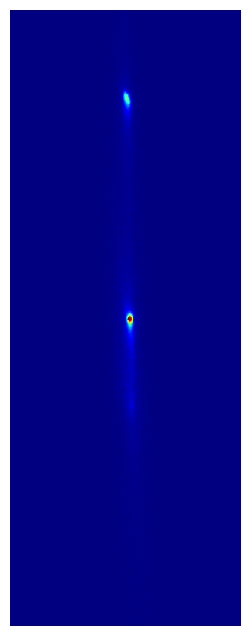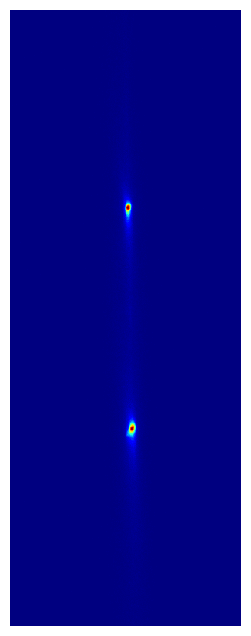
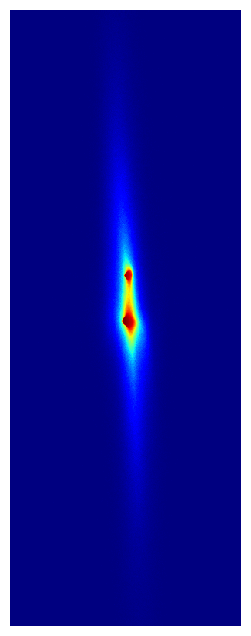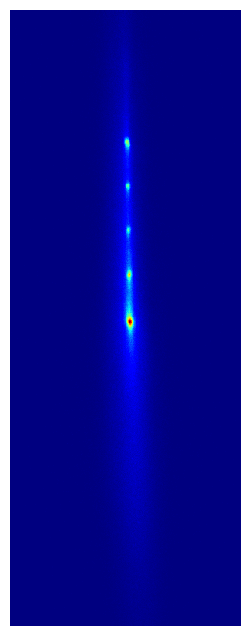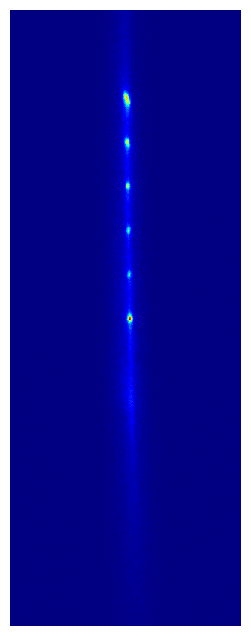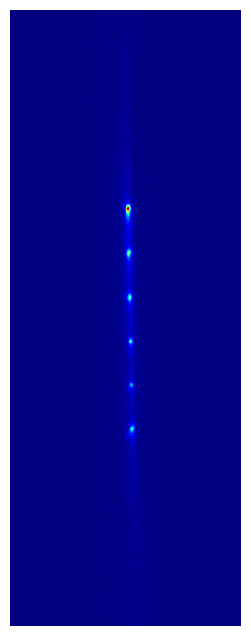
* Sadly this record was short lived, thanks to very exciting complementary results from our good friends in the Ye group, which were posted to the arXiv in coordination with ours. I strongly encourage you to read about them here: http://arxiv.org/abs/2109.12238.
Aedan, Ishita, Matt, and Sam’s paper on charge dynamics in diamond published in Nano Letters!
Congratulations to Aedan, Ishita, Matt, and Sam, whose paper on imaging and controlling charge carrier dynamics in diamond with a single color center has now been published online in Nano Letters!
Here’s a link to the paper: http://pubs.acs.org/articlesonrequest/AOR-AHFGVMFTPSMKYF3BGCAD.
This paper was a collaboration with Dr. Vincenzo Lordi at Lawrence Livermore National Lab, Dr. Ariel Norambuena and Dr. Hossein Dinani at Universidad Mayor, and Prof. Jero Maze at Pontificia Universidad Catolica in Santiago, Chile.
Aedan, Ishita, Matt, and Sam’s paper on charge dynamics in diamond posted to the arXiv!
Congratulations to Aedan, Ishita, Matt, and Sam, whose paper “Probing charge dynamics in diamond with an individual color center” has now been posted to the arXiv!
Congrats to Aedan on passing his prelim exam!

Jacques’ theory paper on Rydberg spin squeezing published in Physical Review A!
Matt, Aedan, and Sam’s paper published in Physical Review Research!
Congratulations to Matt, Aedan, and Sam, whose paper “State-dependent phonon-limited spin relaxation of nitrogen-vacancy centers” has just been published online in Physical Review Research! The paper describes experimental results shedding light on the physical processes limiting the “coherence times” of defects in diamond that are used as quantum sensors and qubits. (Physical Review Research is an open access online journal, so click on through if you’re interested in learning more!)